




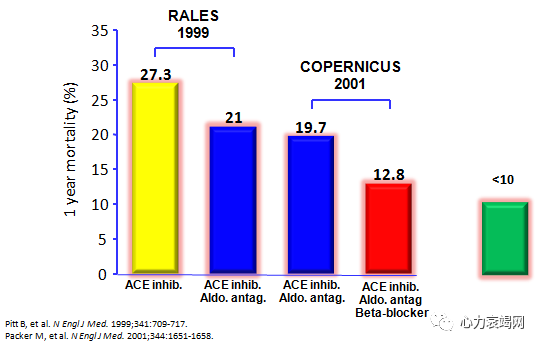
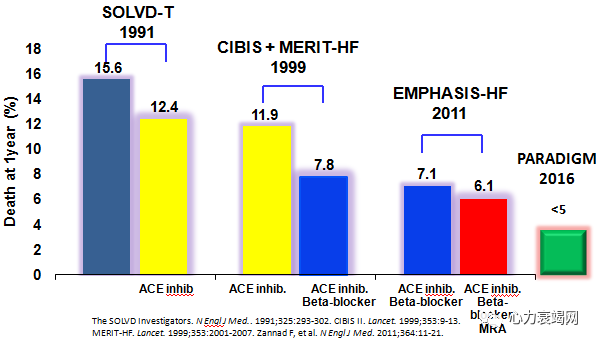
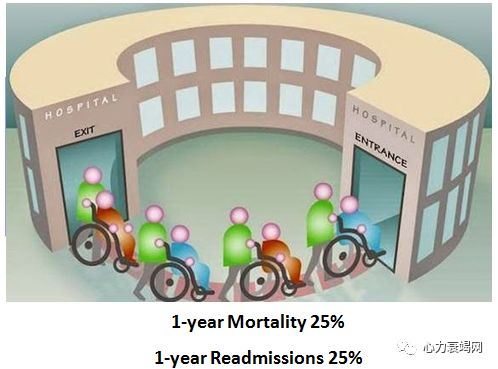
1-yearmortality in patients with systolic heart failure
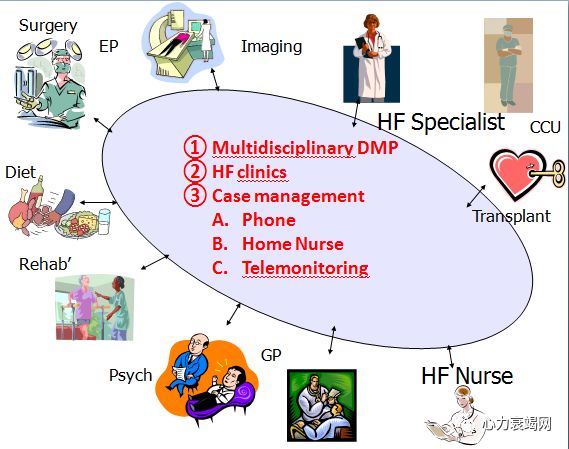

All health and alliedprofessionalsinvolved in the care of a given patient.
–General practitioners/familyphysicians,
–Nurses,
–Cardiologists,
–Dieticians,
–Pharmacists,
–Social workers,
–Physiotherapists
–Palliative care professionals if appropriate.
Integration:
–Social care services SHOULD beintegrated to multidisciplinary care.
Remuneration:
–Anappropriateremuneration SHOULD beprovided to healthprofessionalsfor care coordination roles.
Training
–of all relevant healthcareprofessionals to alignthem to common goals.
Cleargovernance
–designationof coordination andleadership roles
Shareddecision-makingamonghealthprofessionals, facilitated by practical information sharing tools
Efficientinformation systemsthatallow the sharing of patientrecords and monitoring of patient outcome over the entirechain of care
Incentiveschemesthatexplicitlyrewardmultidisciplinaryworking.
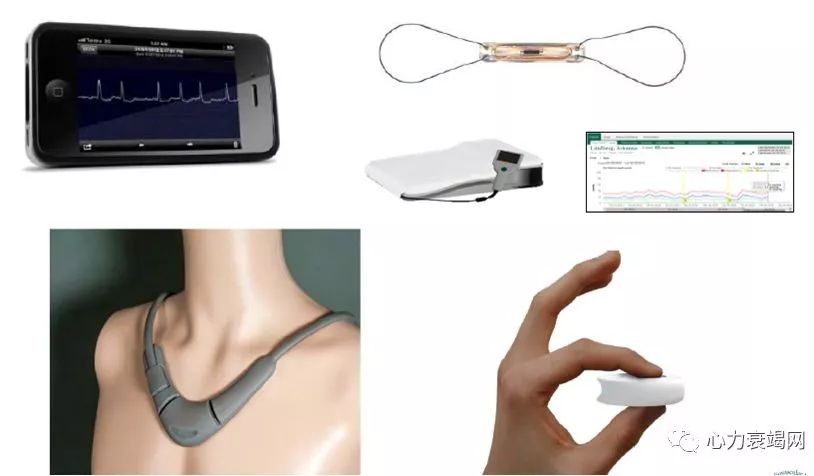
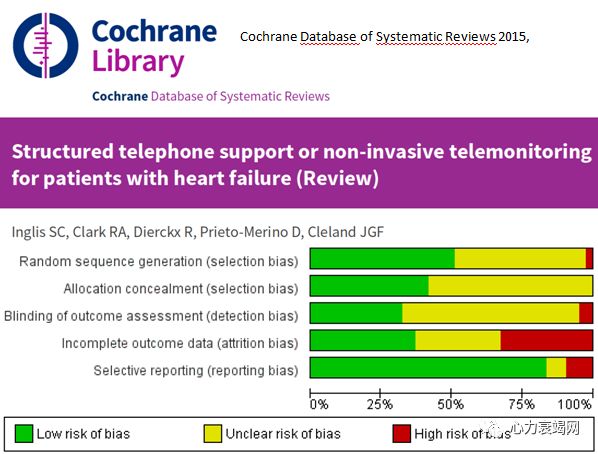
Structuredtelephone support
–22 RCTs (9,222 patients)
–11.6%to 10.1%
–RR 0.87 (0.77 – 0.98)
Non-invasiveTelemonitoring
–17 RCTs (3,749 patients)
–14.5vs. 11.6%RR 0.80 (0.68 – 0.94)
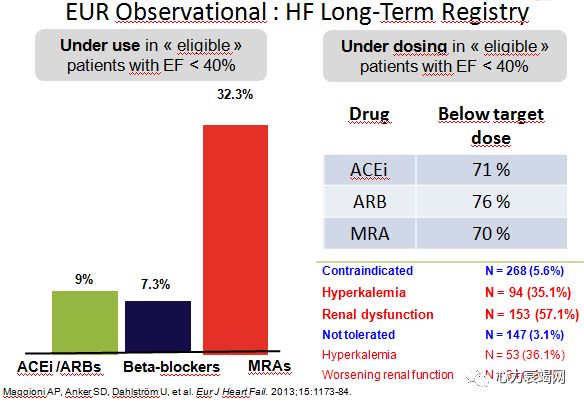
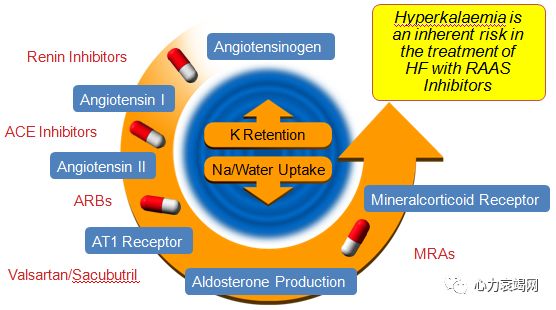
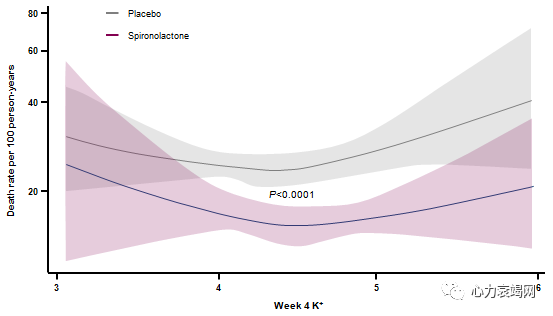
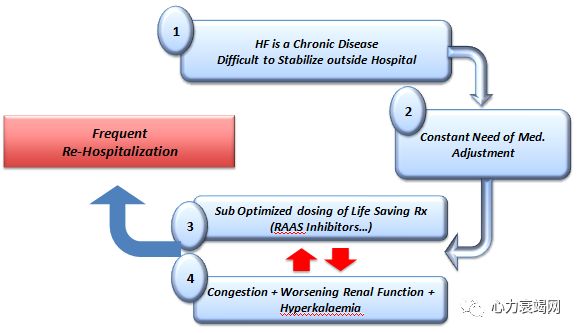
RAASinhibitors are under used and under dosed in dailly practice
Themain reason of under use and under titration is Hyperkalemia.
Suboptimal use of RAAS inhibitors deprives patients from life saving therapy andis associated with poor outcome
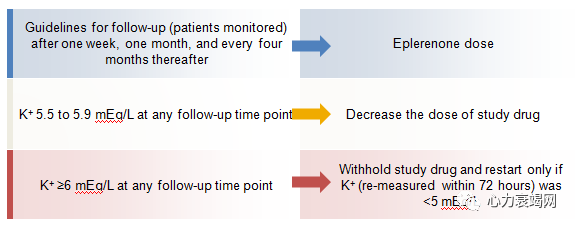
Eliminatingriskfactors
Directlyloweringserum K.
Regularmonitoring of serum K for patients on RAS inhibitorsand MRA antagoniststo optimizedosing and minimize the risk of hyperkalaemia.
New K-loweringmedications
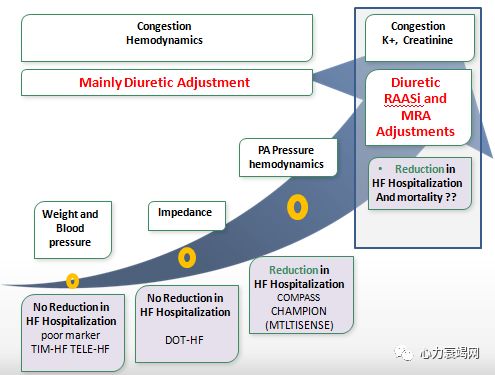
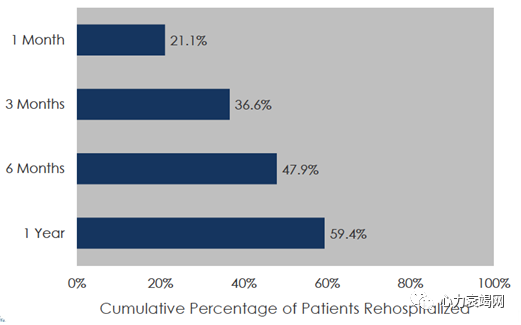
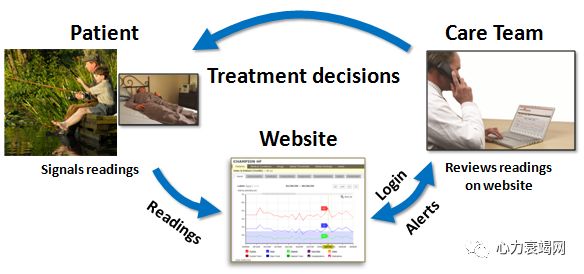
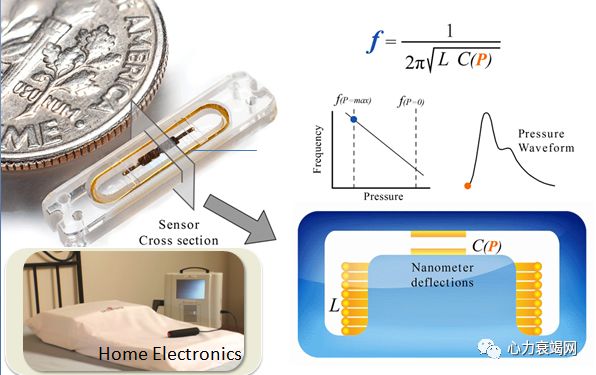
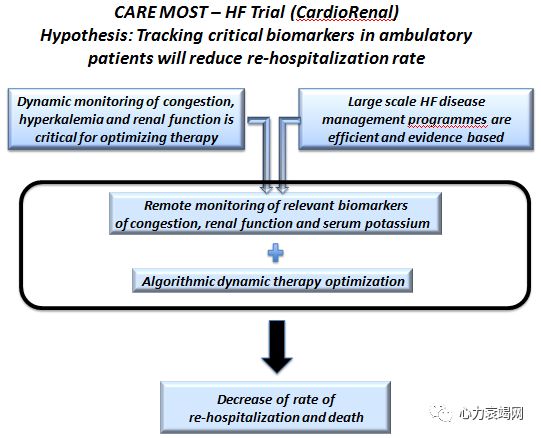
Hypothesis: Tracking critical biomarkers in ambulatory
patients will reduce re-hospitalization rate
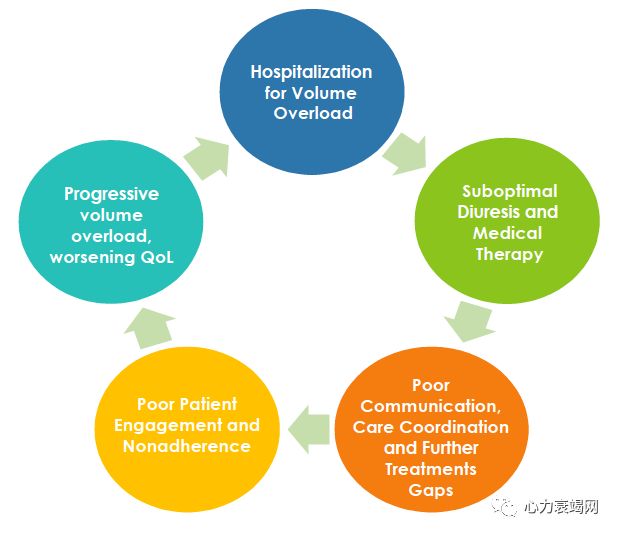
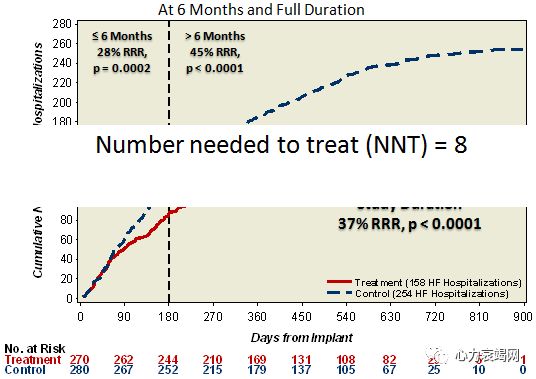
Heartfailure disease management programmes efficacy
– Arestrongly recommended
– Efficacyis based on high level of evidence
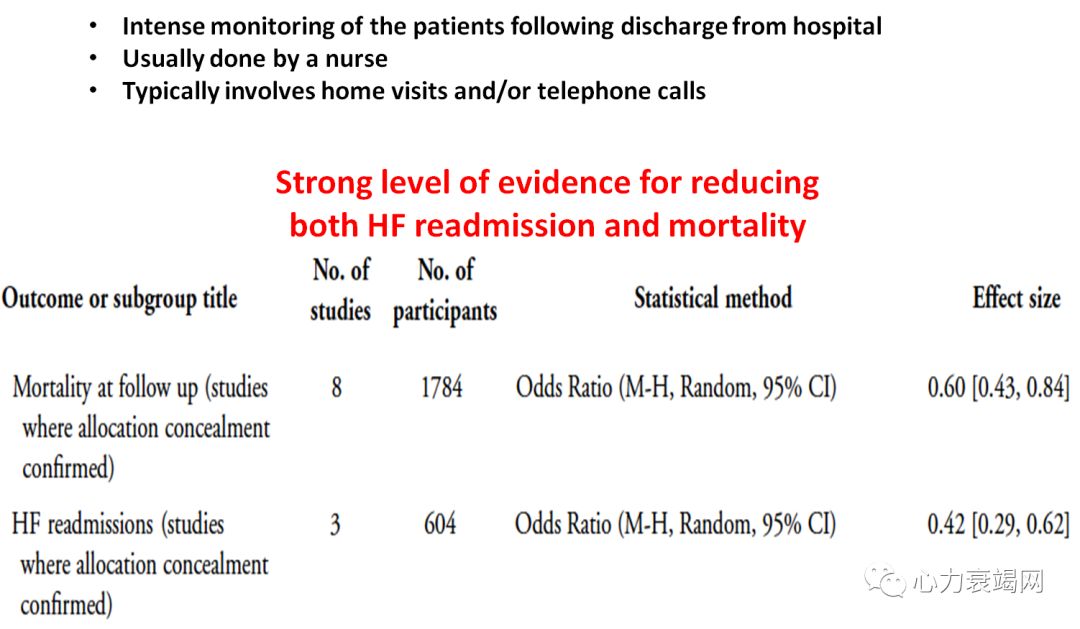
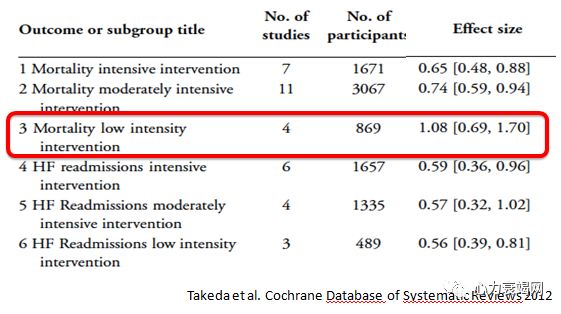
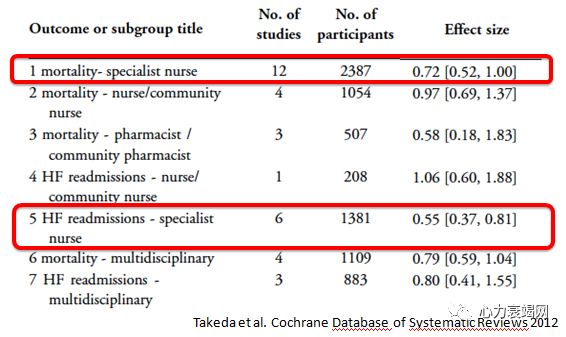
Intensivecase management based on specialised nurse seems to bemost effective in reducing both the rate of HF hospitalisation and of mortality
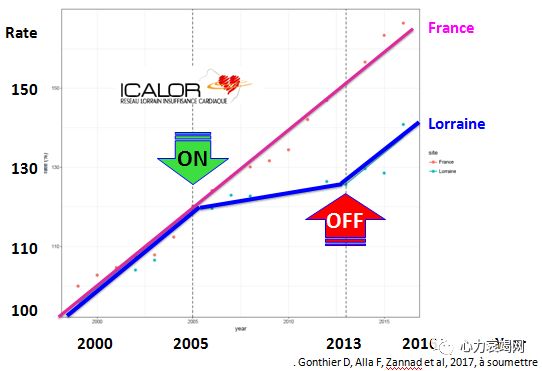
Reallife implementation
– Consistentwith trial evidence
– Costeffective
Adoptionby health care systems is insufficient and should be promoted pro-actively by« payers »
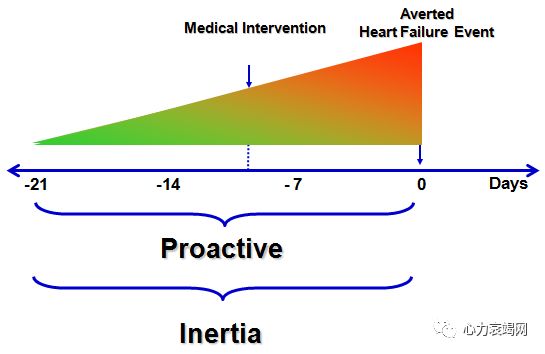
Facilitatingoptimisation of life-savingtherapies, using technology-based remotemonitoring may maximise benefit
专家简介

Faiez Zannad教授
法国洛林大学心血管病研究院
心力衰竭和高血压中心主任
Faiez Zannad is Professor of Therapeutics and Cardiology.
He is at the Head of the Division of Heart Failure, Hypertension and Preventive Cardiology for the department of Cardiovascular Disease of the Academic Hospital (CHU) in Nancy and the Director of the Clinical Investigation Centre (Inserm-CHU) of Nancy since 1995.
He entered the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) in 1996 and is past Chairman of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Working group on Pharmacology and Drug Therapy and past-President of the French Society of Hypertension.
He is the Principal investigator and Member of Steering committees of major large scale trials in human cardiology (RALES, VALIANT, CIBIS, CAPRICORN, EPHESUS, EMPHASIS-HF).
He has served as Co-Editor-in-Chief for Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology, the official journal of the European Pharmacology Societies Federation (EUPHAR).
He chairs and organises annual international meetings on CardioVascular Clinical Trials (CVCT) and on Biomarkers in Heart Failure.