




Early detection or immediatelymonitoring of the new or aggravated patients with HF is very important fortimely therapy
早期发现心衰或心衰加重患者非常重要
there is still lacing a fast,user-friendly, non-invasive methods to allow detection or monitoring of HF andideally cost-effective screening early
目前尚缺乏无创的非接触的心衰探测方法
1. Jessup M,etc. N Engl J Med 2003;348:2007-18.
2. Collins S, etc. J Card Fail 2015;21:27-43
The lower body temperature (BT) maybe related with some poor physical general condition
低体温与一些很差的机体状态相关
Hypothermia could be a useful markerfor predicting worse prognosis in heart failure (HF) patients
低体温是心衰恶化的标志之一
Hypothermia could be a simple and useful markerfor predicting readmission,decreased time to rehospitalization and survival in HF patients
低体温也用于预测心衰患者再入院及生存时间缩短
1.RingF. Diabetes SciTechnol2010;4:857-62
2.NallamothuBK, etc. J Am CollCardiol2006;47:2563-4
3.PayvarS, etc. European Journalof Heart Failure 2013;15:1382-9
4.AhmedA,etc. J Card Fail 2008;14:489-96
5.OmarHR,etc. Int J Cardiol2016;220:729-33
心衰导致心脏低输出量和交感兴奋,因而可能导致低体温和血流再分布
HFpatients with lowercardiac output
highersympathetic-catecholamineand RAAS activity, which resulted in blood flowing reduction and redistribution
mightlead to hypothermiaand abnormal thermal distributions in peripheral tissue
Triposkiadis F,etc. J Am Coll Cardiol2009;54:1747-62
Thecutaneous thermogram and temperature quantification canbe acquired quickly, noninvasively and contact free by an infrared thermal image
红外热像可快速获取人体二维温度分布状态
Thethermal distribution of the body surface is showed in a two-dimensional digitaltable or coded representing in gray-scale or color imaging according to thewavelength of the infrared radiation
红外热像可以灰阶或伪彩色显示

Wedesigned the Facial INfrared thermal Distribution in HeartFailure patients study (Find-HF Study) to evaluate facialhypothermia and abnormal thermal distribution in HF patients based on IRTI inclinical practice
FIND-HF为首个用红外热像评价心衰面部低温和热分布异常的多中心临床研究
The FIND-HF investigation group
Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University Jing HUANG MD
Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Acdemy of Medical Sciences Jian ZHANG MD
Anzhen Hospital, The Capital Medical University Jianzeng DONG MD
First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing MedicalUniversity Suxin LUO MD
General Hospital of Jiangjing Distract, Chongqing Shiquan FU MD
General Hospital of Chongqing Steel Company Henhua DAI MD
Theparticipants of thisstudy were screened from new admitted patients with suspected HF from November,2015 to August, 2017
新住院疑诊心衰的患者进行面部红外检测
N-terminalpro brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) or BNP, LVEF, SimpsomMethod
Diagnosisprocess of HF wasaccording to the guideline of ESC 2012
心衰患者也以EF和HYHA分级进行亚组分析,并申请临床试验注册
The patients in HF group further divided into HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) group (LVEF>40%) and HF with reduced ejectionfraction (HFrEF) group (LVEF≤40%)
also divided into Ⅰ-Ⅳ groups according to the New York Heart Function Assessment(HYHA) class
The Find-HF study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committees of eachhospital, and registered in Clinical.Trials.gov. (NCT02672618)
用红外相机对所有患者进行面部温度采集,病房温度22-28°C
The facialthermograms in all patients were captured using an IRS camera
The camera uses an uncooled microbolometer focal plane array with a resolution of 384×288 pixels and a thermal sensitivity of 0.1 at 30 ℃
Thermography was collected at an appropriate distance, insuring that the margins of the face closed to the sampling frame of the image in the ordinary wards, and the room temperature was 22-28 ℃
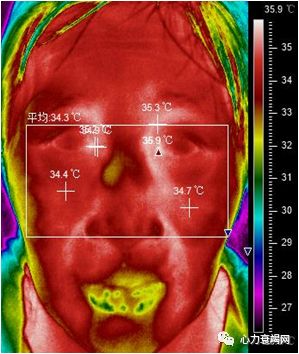
meanfacial temperature (mFT)(平均温度)
temperaturestandard deviation (TSD)(温度标准差)
meaninner canthustemperature (mICT)(平均内眦温度)
meancheek temperature (mCT)(平均面颊温度)
Differencebetween mICT and mCT (DICC)(眦颊温度差)
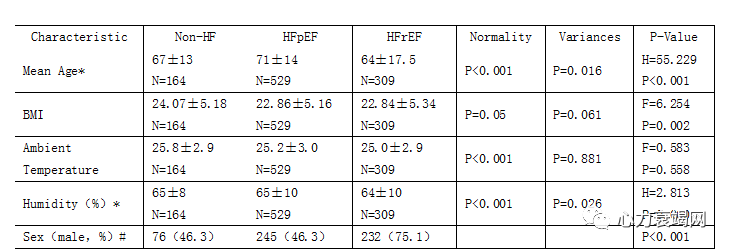
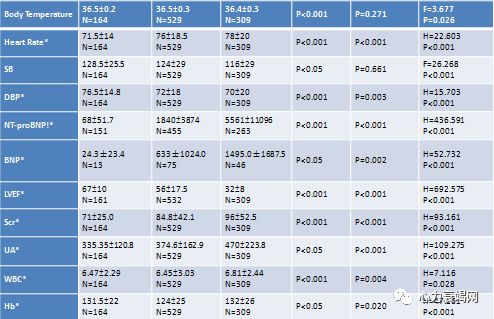
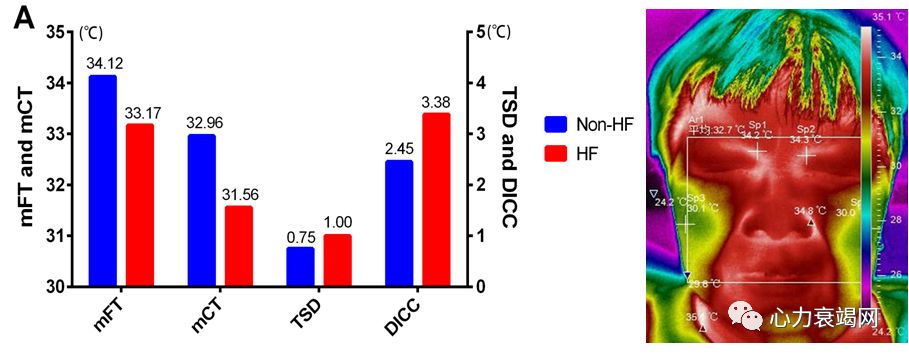
ThemFT and mCT, which represent general and peripheral facial temperature of the patients respectively, were significantly lower in HF group than the Non-HF group (both p<0.001) The TSD and DICC, was significantly higher in HF group (both p<0.001)
心衰患者总体和外周温度显著降低,而温度分布离散度显著增高
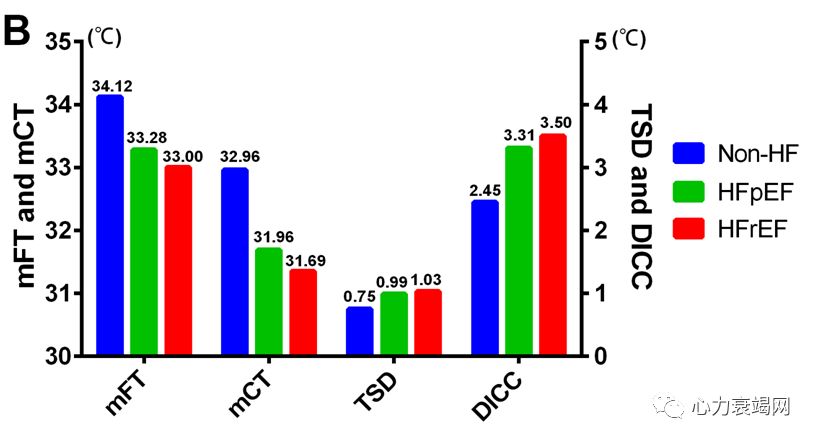
LVEF subgroup, the mFT and mCTwas significantly lower in HFrEF group than HFpEF group (both p<0.001), while the TSD and DICC was significantly higher in HFrEF group (both p<0.001)
LVEF降低亚组温度变化特征更为明显
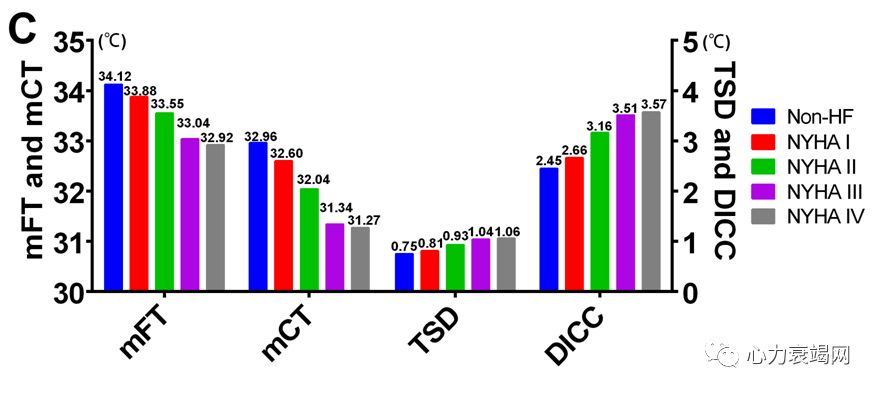
For the NYHA subgroup analysis, the mFT, mCT, TSD, DICC and CTD were significantly different between NYHA Ⅰ-Ⅳ groups (all p<0.001), but was not significantly different between NYHA Ⅰ and Non-HF group. The mFT and mCT was lowest in NYHA Ⅳ group, while the TSD, DICC and CTD was highest in NYHA Ⅳ group
NYHA分级相关亚组显示面部温度变化于症状密切相关
Multivariablelinear regressionresults showed that the mFT was positive correlated with SBP,LVEF, AT and Scr, while negatively correlated withage, sex (male), NYHA classes, MRoL and UA
多元线性回归分析显示,面部温度主要与SBP和LVEF正相关;与NYHA分级和肺部啰音负相关
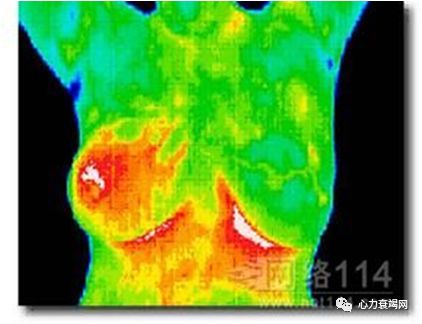
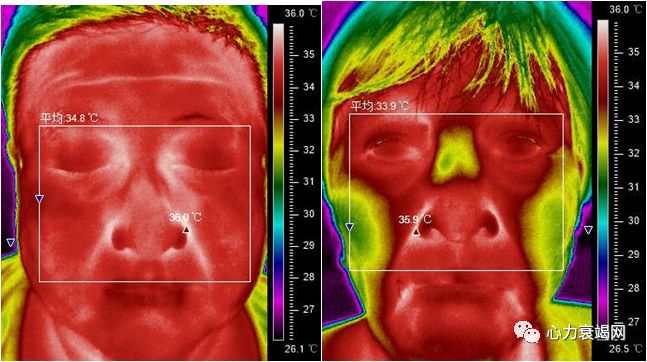
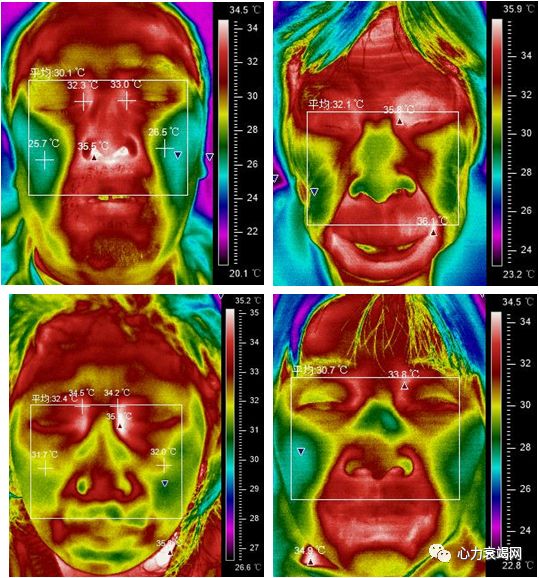
Theincident of Monkey Face sign in HF patients was 60.4%
non-HF patients also presented Monkey Face Sign (19.5%)
the serious HF patients with higher incident of Monkey Face Sign, as in HFrEF(63.8%) and NYHA Ⅳ group (69.8%)
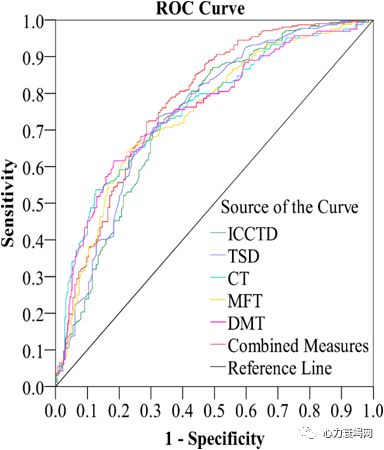
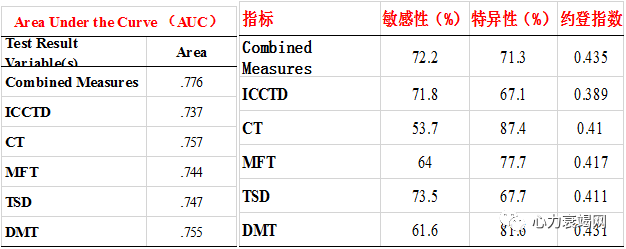
combined parameters of mFT, mCT, TSD, DICC and CTD, multivariate ROC curves with sensitivity of 75.3%, specificity of 62.8%, and value of area under curve (AUC) of 0.747 in discriminating HF from Non-HF patients
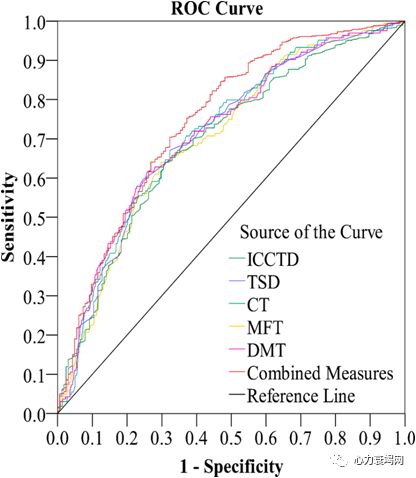
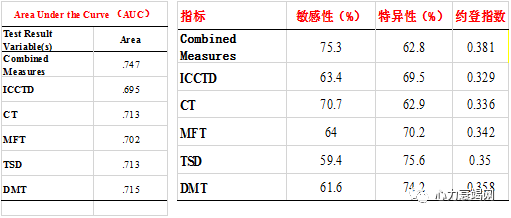
The sensitivity, specificity and AUC value were 79.4%, 64.6% and 0.774 respectively in discriminating NYHA Ⅲ-Ⅳ from Non-HF patients
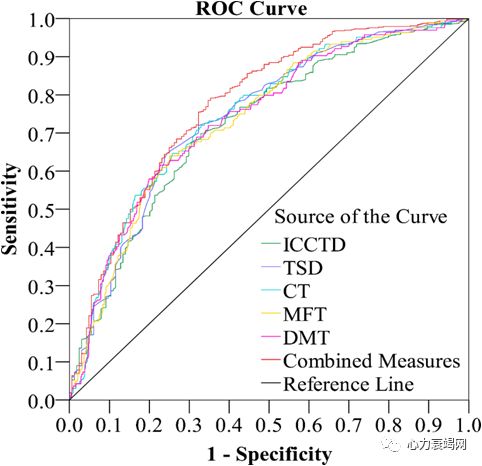
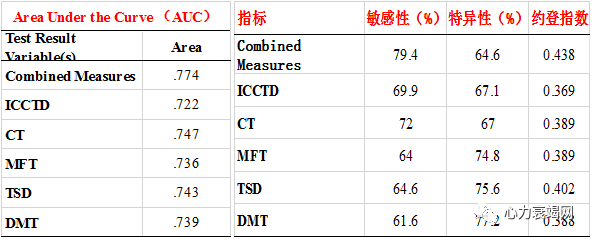
while were72.2%, 71.3% and 0.776 respectively in discriminating HFrEF from Non-HF patients
The Find-HF Study is the first multicenter study to evaluate facial thermal distribution in HF patients based on a noninvasive IRTI
The main findings showed an appearance of hypothermia, increase of dispersion and abnormal facial temperature distributions in HF patients
The Monkey Face Sign on IRTI, revealed a characteristic of central thermal distribution on face, was more frequent in the HF patients
With combined-parameter of mFT, mCT, TSD, DICC and CTD, the sensitivity, specificity and AUC value were 66.1%, 73.2% and 0.752 respectively in discriminating HF from Non-HF patients, and were 79.3%, 73.2% and 0.825 respectively in discriminating HFrEF from Non-HF patients
Facial pallor is found by inspectionin some HF patients with low hemoperfusion
临床有时可发现面部低灌注
mFT was positive correlated with SBP and LVEF, whichindicated a better hemoperfusion
红外技术可更多地发现患者面部低灌注现象
NYHA classes and MRoL, which related to the severity and symptoms of HF,contributed to the reduction of mFT
研究揭示NYHA分级和肺部啰音与面部低灌注联系更为密切
Theinner canthus, closed to the core temperature of the body, was less affected by the perfusion redistribution
内眦接近人体核心温度
Thecheek, is mainly reflecting peripheral circulation, and wasobviously decreased in the HF patients with perfusion redistribution
面颊温度较好反映外周循环
The results showed thatDICC was significantly higher in the HF patients
The FTDA between HF and Non-HFpatients was mainly in the cheek, supporting facial mCT as hypothermal value measurement in HF patients
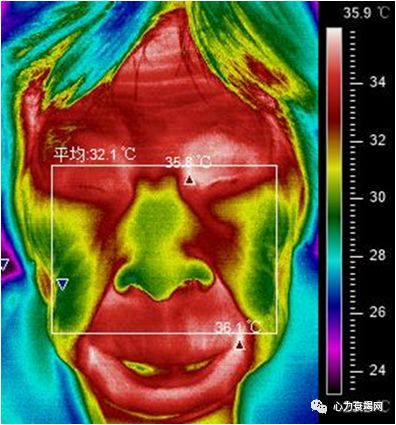
We believe that the Monkey Face Signisn’t peculiar to HF patients and like to surmise it more related with sympathetic activity
我们认为,“猴脸”并不是心衰患者所特有的,更倾向于将其与交感神经活动联系起来。
We assuming that isn’t all HF patients with enough sympathetic tone for flowing redistribution and the facial thermal redistribution may present in health subjects for physiological regulation
我们假设,并不是所有的心衰患者都有足够的交感神经张力来进行再分配,而面部热再分配可能存在于健康主体的生理调节中。
thepresentnon-controlled, non-double-blinded and observational study limits its clinicalimportance, correlation between IRTI detection and prognosis on the HF patientsshould be researched next study
只是观察性研究,未反映动态变化
somefactors cansignificant interfere with the discrimination and analysis of IRTI, asvasoactive agents used, sweating condition, ambient temperature, etc., may leadto certain heterogeneities, which might negatively impact evaluation value for HF
红外技术易受到药物、出汗、环境温度等影响
the data of two-dimension temperature and IRTI haven’t beenfull used still, further analytical method, such as machine learning etc., needto be explored to improve diagnostic value of the IRTI in detection of HF patients
影像包括的信息尚未充分发掘
The Find-HF study showed a facial hypothermia,thermal dispersion increase and abnormal distributions in HF patients
FIND-HF研究揭示心衰患者存在的面部低温和分布离散现象
The facial thermal distribution evaluation may furtherexplore as a noninvasively and non-contact strategy for detection andmonitoring of new or aggravated HF patients in clinical practice
面部红外热像可进一步探索用于新发和加重的心衰患者的探测和监测
专家简介

重庆医科大学附属第二医院
重庆医科大学附属第二医院心血管内科副主任、主任医师、教授、博士研究生导师、中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会委员、中国医师协会心血管转化医学专委会副主任委员、重庆老年学会心脑血管病分会副主任委员、中华医学会心血管病分会高血压学组委员、重庆市高血压学组副组长、重庆医科大学介入超声研究室主任、重庆生物医学工程学会常务理事。长期从事高血压、冠心病、介入心脏病学及医学超声等工作。在高血压治疗、介入医疗器械研发、超声诊疗等领域有所建树。在JACC、IJC等发表论著80余篇,国家发明等专利授权10余件。