


在“2018深圳心力衰竭国际发展论坛暨心力衰竭治疗研讨会·深圳站”会议上,来自乔治华盛顿大学医学院的Gurusher Panjrath教授为我们带来了"Guideline to Clinical Practice: Treatment Strategies in Heart Failure(临床实践指南:心力衰竭的治疗策略)"的精彩报告。

Epidemiology of Heart Failure
2016 AHA/ ACC/ HFSA HF practice guidelines Update
Mechanisms of action
Clinical Trials
54yoAsian American man, non ischemic CM, EF 28%, diagnosed 2 yrback. BIV/ICD
2hospitalizations, has dyspnea walking in park, nipple tenderness with Aldoantagonist
Meds:Metoprololsuccinate100 QD, Furosemide 80, Enalapril 10 mg BID, Exam:BP 102/80 mmHg, HR 52 bpm, JVP~7, no S3/S4. no edema
Pt wants to know how he is going to do?
A) I don’t know!
B) You will do really well
C) You will likely not be around
Wide variation inmortality based on geographical area
Risk for CV death higherfor HFrEF
Hospitalizations are on the rise
Mortality slightly improved (likely from GDMT and ICD) but still high
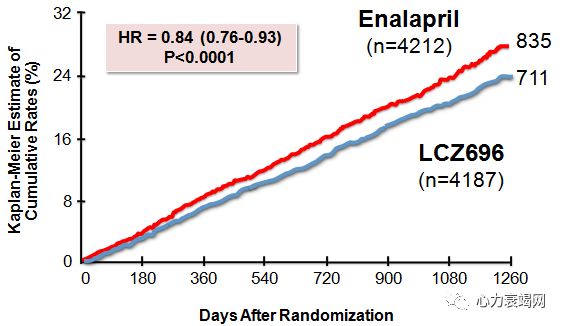
26.5% of patients randomized to enalapril in PARADIGM trial had CV death or HF hospitalization as 1st event
Of all patients randomized to enalapril, the absolute risk of CV death as a first event was 10.9%
Whatwill be the next best step ?
A) Increase beta blocker
B) Add aldosterone antagonist
C) Switch to Sacubitril/valsartan or neprilysin inhibitor
D) Do nothing
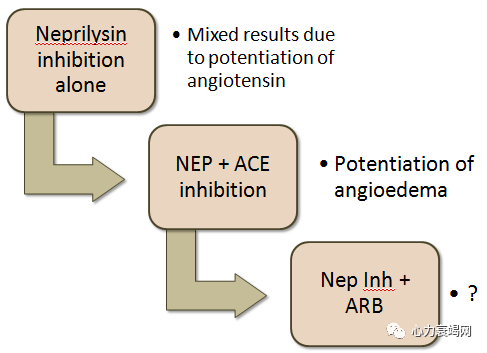
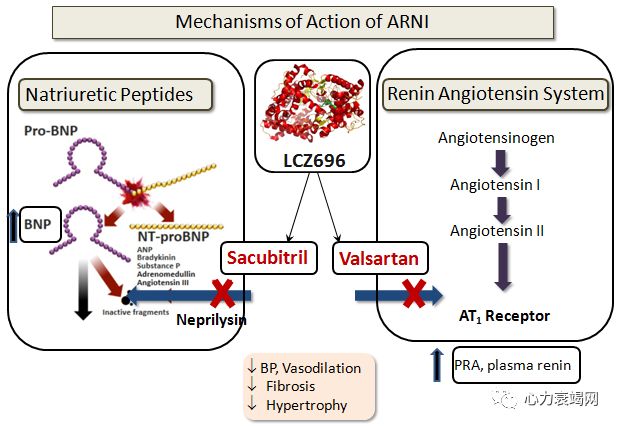
Neprilysin Inhibition and ARNI:
Evolution

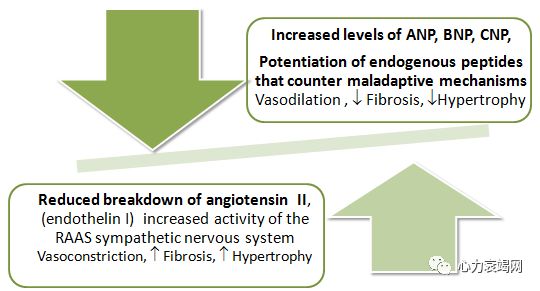
The antihypertensive effects may be offset by an increased activity of the RAAS and sympathetic nervous system and/or by downregulation of ANP receptors.
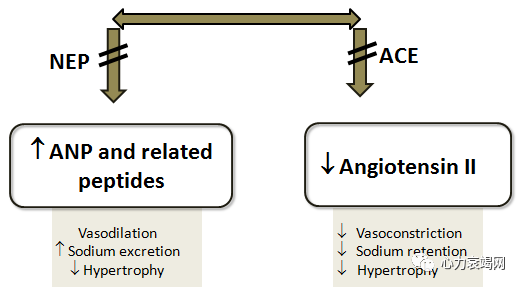
synergistic effect
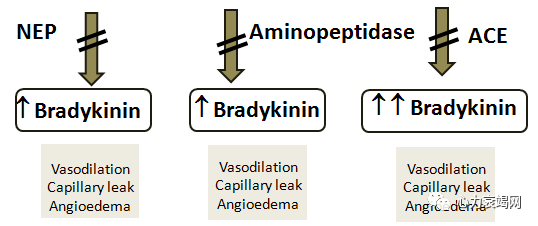
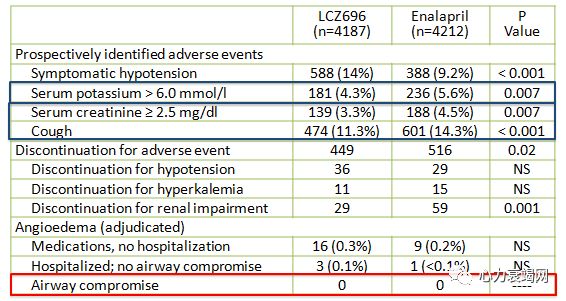
↑ ↑ ↑ increased angioedema
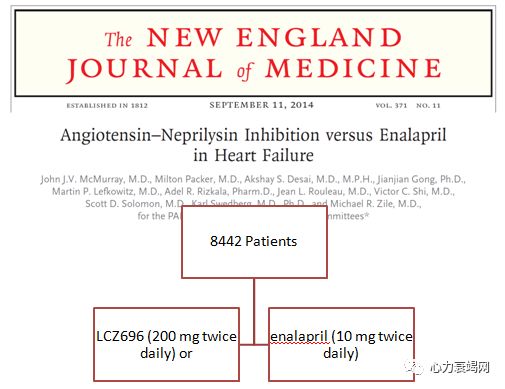
NYHAclass II-IV (less than 1 % NYHA IV) heart failure
LVEF≤ 40% then ≤35%: 2/3 pts EF≤ 35 %, 1/3EF 35-40 %)
BNP≥ 150 (or NT-proBNP ≥ 600)
Guideline-recommendeduse of β-blockers , MRA,
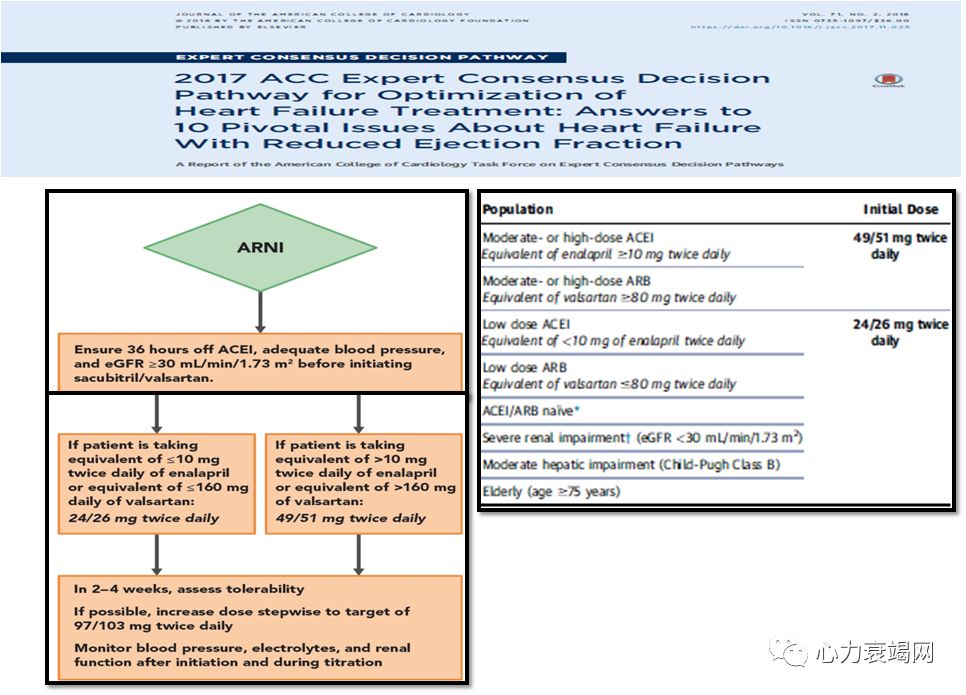
Background therapy to include ACEi of ARB equivalent to enalapril 10 mg/day at least for 4 weeks
Systolic BP ≥ 95 mm Hg, eGFR ≥30 ml/min/1.73 m2 and serum K ≤ 5.4 mEq/Lat randomization
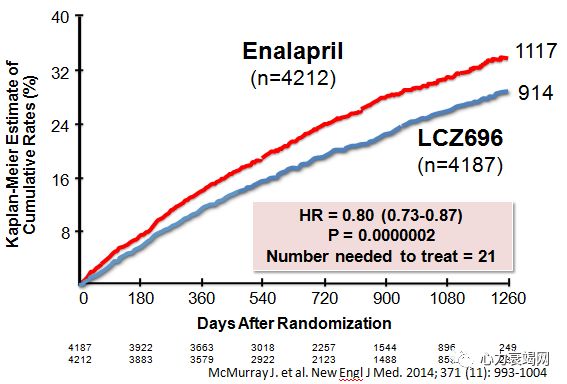
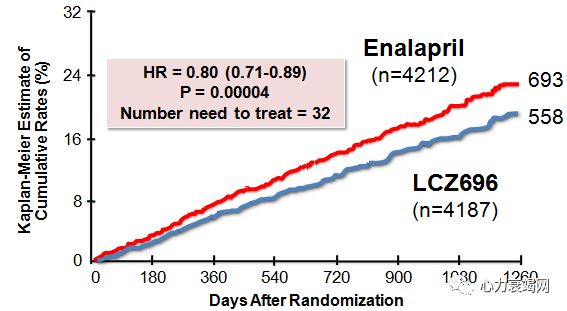
Both SCD(HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.68-0.94, P = 0.008) and death due to worsening HF(HR 0.79, 95% CI 0.64-0.98, P = 0.034) were reduced by treatment with LCZ696 comp with enalapril. Death due to MI or stroke not different (infrequent)

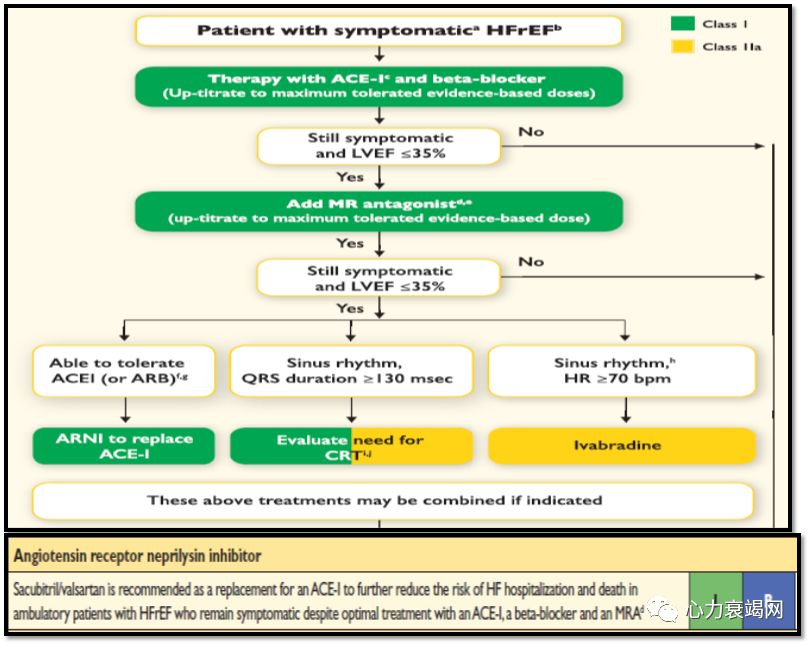
Whento switch to ARNI? – symptomatic HF, on ACE/ARB
ARNIor Beta blocker First? – not tested
Tolerabilityand dosing of ARNI in Asians? Data missing
ARNIin Class IV HF- ongoing studies
ARNIin HFpEF- ongoing studies
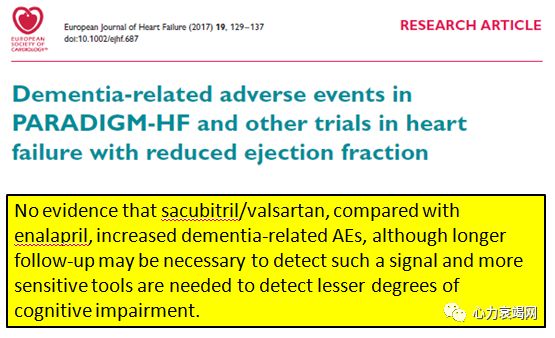
Longterm- beta amyloid deposition?- appears to be safe

If ion channel (the funny current) is highly expressed in spontaneously activecardiac regions, such as the sinoatrial node, the AV node and the Purkinje fibers. The funny current isa mixed Na/ K current that activates upon hyperpolarization at voltages in thediastolic range

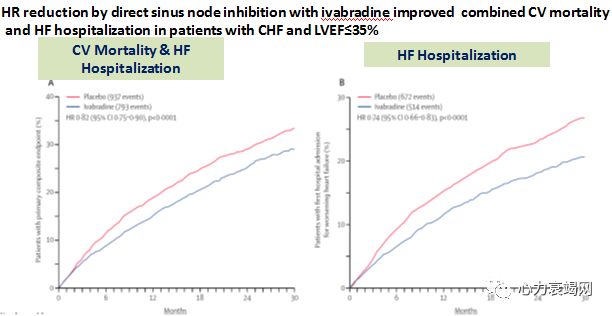
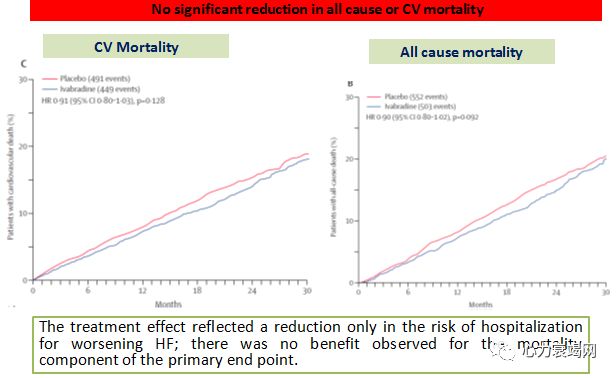
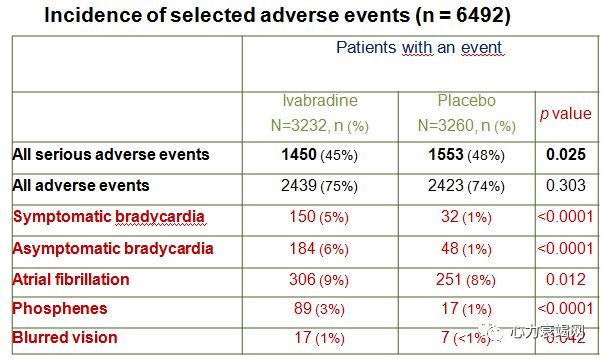
NYHA II–IV, SR rateof ≥70 bpm randomized to ivabradine added to background therapy including abeta-blocker (90%), and an MRA (60%).
Only26% of patients were on full-dose β-blocker

2016 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update on New Pharmacological Therapyfor Heart Failure ACC/AHA/HFSA, A Report of the American College ofCardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Failure Society of America, YancyCW, et al. JAm CollCardiol.

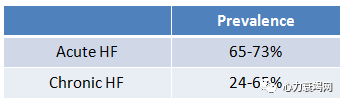
Irondeficiency (ID) is most common nutritional disorder in the world
Commonin HF
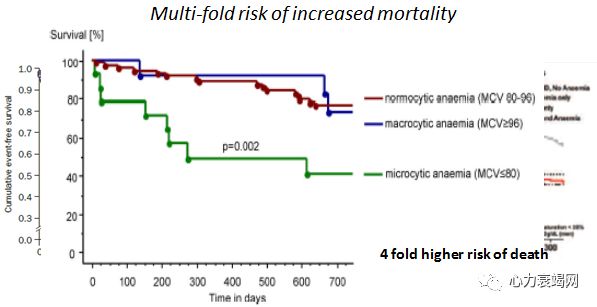
Irondeficiency, both with and without anemia, isassociated with adverse clinical outcomes
Variableprevalence due to lack of standard criteria for ID

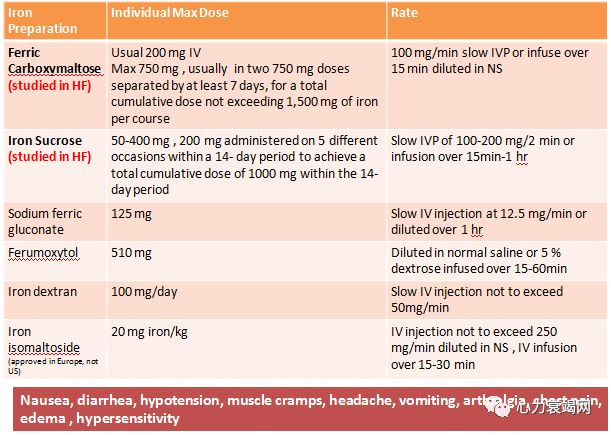
Convenient,readily available and inexpensive, butoral iron is not absorbed well, particularly in patients
Elevatedhepcidin prevents iron absorption by reducing transmembrane ferroportin on enterocytes
Tolerabilityand compliance with of oral iron is low due to GI side effects
largest phase 2 ,double blind RCT
225 patients withNYHA class II-IV HF with HFrEF
Hb 9-15 g/dL (men) or9-13.5 g/dL women) and ID (ferritin 15-100 ug/Lor 100-299 ug/L with TSAT <20%)
oral ironpolysaccharide 150 mg twice daily or placebo
At 16 weeks, there was no significant difference in
primary end point: change in peak VO2 from baseline,
Or secondaryendpoints : 6MWD, NT-proBNP levels or KCCQ score
oral iron increasedTSAT, ferritin and hepcidin, and reduced solubletransferrin receptor levels
Inadequate repletion of iron stores with oral iron despite large doses
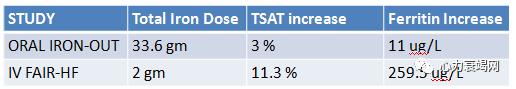
Higher baseline hepcidin levels associated with lessimprovement in TSAT and ferritin
Higher hepcidin levels may limit responsiveness to oral iron,inhibit duodenal iron absorption
Two new therapies for HF approved ; both are novel, first-in-class agents
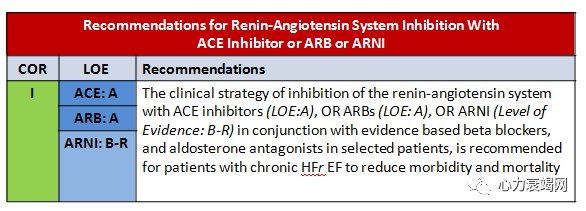
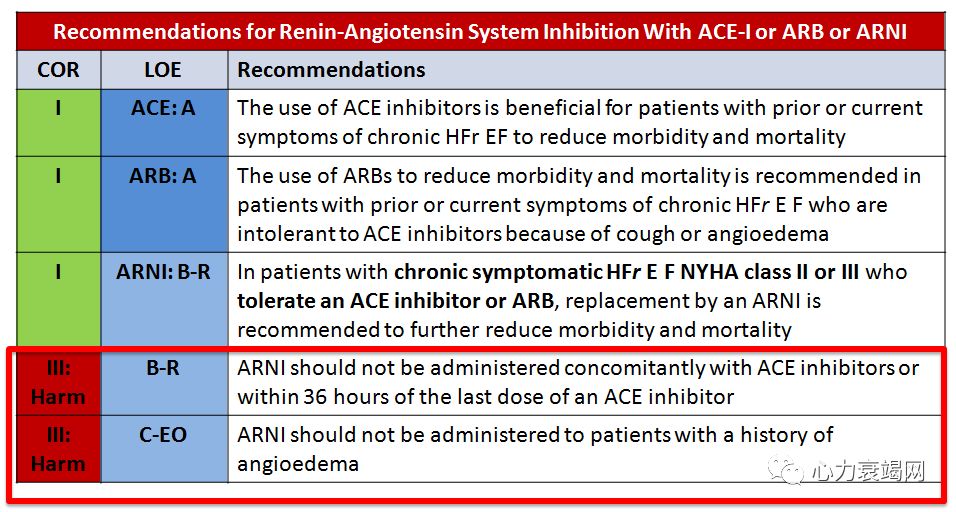
- In HFrEFNYHA class II or III pts who tolerate an ACE inhor an ARB, replacement with an ARNI is recommended to further reduce morbidity and mortality
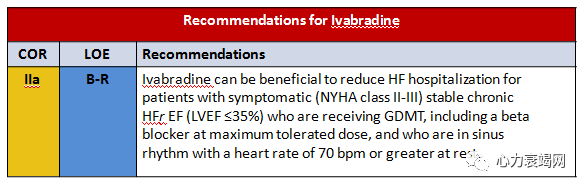
- Ivabradine can be beneficial in stable chronic symptomatic HFrEFwith elevated heart rate to further reduce morbidity
Beta blockers continue to be a mainstay inthe treatment of heart failure with reduced EF
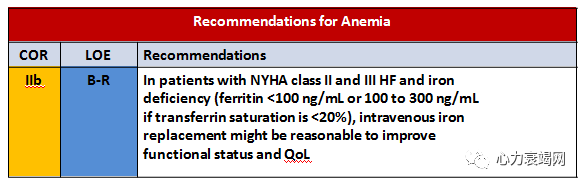
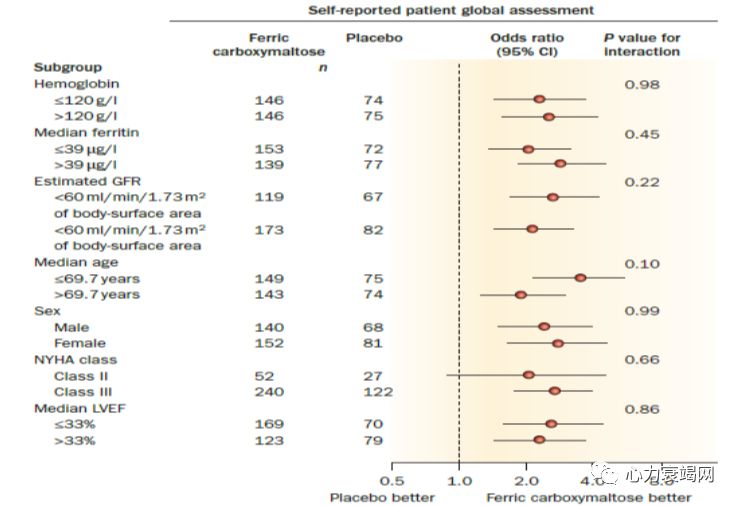
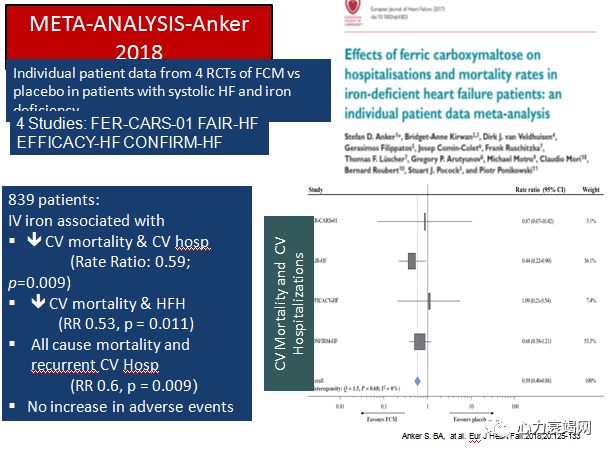
IV iron may be considered for those with iron deficiency and symptomatic HF
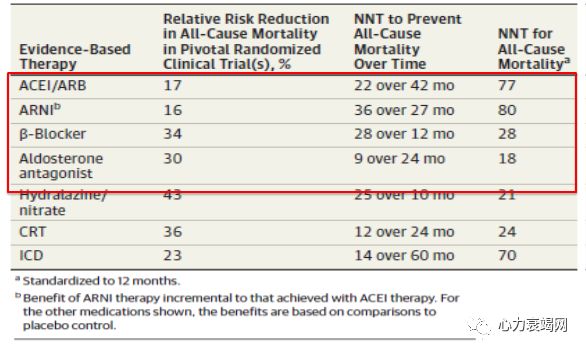
Evidence-based guideline directed management should beused for all patients with HF
Management requires recognition of indications,contraindications, side effects and individualization of therapy
Effective implementation of guideline-directed best quality care reducesmortality, improves QOL and preserves health care resources.
Future studies to answer: nonpharmacological therapy (exercise,stem cells, rehab, mind body medicine) , treatment of HFpEF and hospitalized HF
专家简介

Gurusher Panjrath教授
乔治华盛顿大学医学院
医学博士,FACC, FAHA,主任,心力衰竭和机械支持项目,华盛顿特区乔治华盛顿大学医学院医学副教授,美国心脏病学院,心力衰竭和移植科